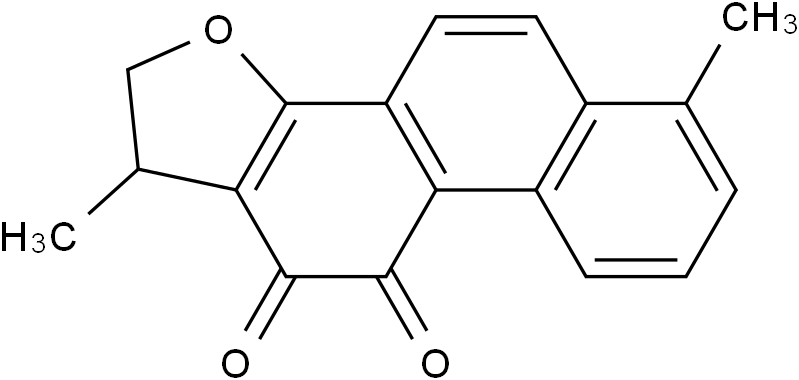
Dihydrotanshinone I
CAS No. 87205-99-0
Dihydrotanshinone I( DHTS | Dihydrotanshinone I )
Catalog No. M16341 CAS No. 87205-99-0
Dihydrotanshinone I (DHTS) was previously reported to exhibit the most potent anti-Y activity among several tanshinones in colon Y cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 83 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 172 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 249 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 412 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 888 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydrotanshinone I
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydrotanshinone I (DHTS) was previously reported to exhibit the most potent anti-Y activity among several tanshinones in colon Y cells.
-
DescriptionDihydrotanshinone I (DHTS) was previously reported to exhibit the most potent anti-Y activity among several tanshinones in colon Y cells. Its cytotoxic action was reactive oxygen species (ROS) dependent but p53 independent.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDHTS | Dihydrotanshinone I
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetROS
-
RecptorROS
-
Research AreaCardiovascular Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number87205-99-0
-
Formula Weight278.31
-
Molecular FormulaC18H14O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Chloroform
-
SMILESCC1COC2=C1C(=O)C(=O)C3=C2C=CC4=C3C=CC=C4C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Wang L, et al.Phytomedicine. 2015 Nov 15;22(12):1079-87.;
molnova catalog



related products
-
Febuxostat
Febuxostat is a Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of febuxostat is as a Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor.
-
Heme Oxygenase-1-IN-...
HO-1-IN-1 is a heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) inhibitor (IC50: 250 nM).
-
Baicalein
The flavonoid component of Nepalese and Sino-Japanese crude drugs.1,2 Baicalein,a major flavone of Scutellariae baicalensis,inhibits the 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism,which inhibits Y cell proliferation and induce.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


